What Is Red Light & Near-Infrared Light Therapy? Science, Benefits & How to Use It
2026 Jan 16th
Discover a gentle, science-backed path to cellular healing, skin vitality & whole-body recovery
Summary
Red light and near-infrared light therapy use non-invasive wavelengths of light to support healing, cellular energy, and regeneration from the inside out. Known clinically as photobiomodulation (PBM), these therapies have been studied for their powerful effects on skin, muscle, joint, and neurological health. Backed by PubMed-cited clinical research and trusted by both health-conscious individuals and elite athletes, this guide explores how red and near-infrared light therapy work, their science-backed benefits, and how to incorporate them into a radiant wellness lifestyle.
What Exactly Is Red Light and Near-Infrared Light Therapy?
Red and near-infrared light therapy, often called photobiomodulation, is a restorative, non-invasive treatment that uses visible red and invisible near-infrared wavelengths to energize and heal the body’s cells.
Unlike ultraviolet rays, which can harm skin, or lasers, which can be aggressive, these gentle light therapies are non-ionizing and safe when used appropriately. Instead of creating heat or damage, they nurture the body’s biology to function more efficiently. It's like photosynthesis for your cells.
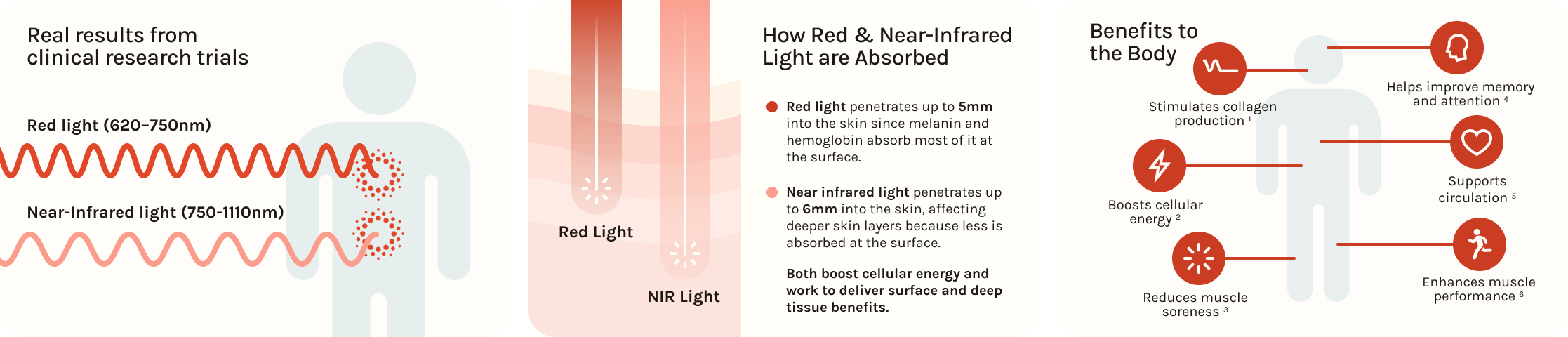
Wavelengths of red and near-infared light impact the benefits:
- Red light (typically 630–660 nm) targets the surface layers of the body. It’s ideal for improving skin tone, stimulating collagen, calming inflammation, and accelerating wound healing.
- Near-infrared light (commonly 810–850 nm) penetrates deeper, through muscle, joints, and even brain tissue, making it a favorite among those seeking recovery, pain relief, or cognitive clarity.
Both wavelengths fall within the “optical window,” a range of light that can effectively pass through skin and tissue for therapeutic impact.
How Red Light & Near-Infrared Light Therapy Works
Think of this therapy as cellular recharging. The light enters the body, is absorbed by the mitochondria (your cell’s energy centers), and boosts production of ATP, the fuel your body uses for everything from muscle movement to skin renewal.
Note on Efficacy: Not all wavelengths are equally effective. Clinical studies show that light between 630–660 nm (red) and 810–850 nm (near-infrared) offers the most consistent therapeutic benefits. Light in the 700–750 nm range has shown limited biochemical activity and is generally not recommended for therapeutic use.
How Light Supports Healing:
- Enhances ATP Production: Energizes mitochondria for improved cellular metabolism1
- Improves Circulation: Stimulates nitric oxide, leading to better oxygen and nutrient delivery2
- Reduces Inflammation: Promotes antioxidant activity that calms chronic inflammation3
- Accelerates Regeneration: Encourages tissue repair and collagen formation4
This gentle intervention works in harmony with the body’s own intelligence, enhancing function, not overriding it.
How Deep Does the Light Really Go? Tissue Penetration, Explained
If you’ve ever wondered how red light and near-infrared light actually make a difference in your body, the answer lies in their ability to reach your cells — not just your skin.
Light doesn’t pass through tissue equally. Red light, with its shorter wavelength, stays closer to the surface. Near-infrared light, with its longer wavelength, travels further. But both play essential, complementary roles in whole-body wellness.
Tissue Penetration Depth by Wavelength
(Based on Hamblin, 2017 — Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery, 2017)
| Light Type | Wavelength Range | Depth of Penetration | Primary Target Areas |
| Red Light (Visible) | 620–700 nm | Skin surface, up to 5mm |
Skin, collagen layer, superficial capillaries, wound sites |
| Near-Infrared (NIR) | 800-850 nm | Skin surface, up to 6mm | Muscles, fascia, joints, nerves, deeper soft tissues |
| Deep Near-Infrared (NIR) | 904–1064nm | Deeper tissues, up to 20mm | Deeper blood vessels, connective tissues, circulation pathways |
These estimates reflect real-world measurements in human skin. Factors like skin tone, tissue density, and the strength of the light source all play a role. Red light stays skin-deep, while near-infrared light is your go-to for reaching deep tissue layers.
Why Does Tissue Penetration in Red Light Therapy Matter
Red light therapy, with its shallower penetration, is beautifully suited for surface-level transformation. It stimulates fibroblasts, the cells responsible for collagen and elastin, making it a powerful tool for skin rejuvenation, scar healing, and calming inflammation that lives just beneath the surface. It's also where many of our health-conscious clients begin their journey with light therapy: visible results, radiant glow, and a deeper connection to the body's rhythms.
Near-infrared light, by contrast, becomes essential for our clients seeking deeper healing. It reaches the fascia, joints, and muscle layers, perfect for performance-minded individuals recovering from intense training or managing chronic pain. The therapy feels like a whisper to the nervous system, supporting relaxation, circulation, and cellular repair where you need it most.
Our customers, whether wellness-oriented or performance-driven, often pair red and near-infrared light with our infrared saunas. Why? Because this combination supports surface restoration and deep cellular recovery, all in one seamless routine. It's not about chasing quick fixes. It's about building a long-term relationship with your health, one session at a time.
Is Red Light Therapy and Near-Infrared Light Therapy Safe?
Yes, when used correctly. Red and NIR light therapy has been shown to be non-invasive, non-thermal, and free from harmful UV radiation. Most studies confirm that PBM, especially when delivered through LEDs at therapeutic doses, has a very low risk profile. Like any wellness tool, the key is dose control. More is not always better. That’s why premium, clinically-aligned devices matter.
What Are the Benefits of Red Light and NIR?
The benefits of red and near-infrared light therapy are not just theoretical. They’re being validated by a growing body of research and experienced firsthand by thousands of Radiant Health customers. These wavelengths support a wide range of biological functions that align with the goals of skin health, recovery, longevity, and whole-body balance.
- Skin Health & Beauty: Red light increases collagen density, reduces fine lines, and enhances circulation to promote a visibly more radiant complexion.4
- Pain Relief & Inflammation: Near-infrared light helps reduce chronic joint pain, muscle soreness, and tissue inflammation, making it ideal for anyone managing an active lifestyle or long-term discomfort.5
- Injury Recovery: Both wavelengths accelerate healing of wounds, ligaments, and soft tissues by enhancing local blood flow and stimulating regenerative pathways.5
- Cognitive Clarity & Mental Well-Being: Studies suggest near-infrared light may help support brain health, improve mood, and even aid in managing cognitive decline by increasing cerebral blood flow and reducing oxidative stress.
- Sleep & Energy: By resetting circadian rhythms and calming the nervous system, light therapy can promote deeper, more restorative sleep and greater daytime energy.
These effects aren’t isolated, they build over time. Like meditation or movement, consistency is key to unlocking lasting results.
How Radiant Health Clients Use Red Light & Near-Infrared Light
Whether seeking vibrant longevity or peak recovery, light therapy supports both journeys beautifully.
The Wellness-Seeking Professional
For our wellness people, light therapy is part of a sacred morning ritual or a mindful end-of-day wind-down. It helps them:
- Support youthful skin and smooth texture
- Balance mood during seasonal transitions
- Reconnect with their bodies after long hours at a desk
- Ease into restful sleep
The High-Performer & Athlete
For performance-driven people, from serious runners to weekend warriors, near-infrared therapy is their secret weapon for:
- Faster recovery after intense workouts
- Easing joint soreness and muscle fatigue
- Preparing the body before training sessions
- Reducing the risk of injury
They often pair sauna and light therapy as part of a holistic recovery protocol . Stacking modalities for maximum benefit. It’s a system that works in harmony with their physiology, not against it.
What to Look for in a Red & Near-Infrared Light Therapy Device
Choosing a light therapy device is about more than convenience: it’s about trust, quality, and results. Here's what you should look for:
- Clinically Validated Wavelengths: Ensure the device uses wavelengths that are proven in the literature: 630–660 nm for red light and 810–850 nm for near-infrared. Avoid devices that advertise vague or unverified ranges like 700–750 nm.
- Power Density & Irradiance: More isn’t always better. Look for a device that delivers consistent, safe power output (typically in the range of 20–100 mW/cm²) to ensure therapeutic effectiveness without overheating the skin.
- EMF & Safety Standards: Choose a low-EMF device that’s been third-party tested for electrical safety and electromagnetic field exposure, especially important for frequent, close-range use.
- Coverage & Design: Consider your goals. A targeted device is great for spot treatment, while a full-body panel or integrated sauna lighting offers systemic benefits.
- Transparent Testing & Certifications: Trust brands that back their claims with transparent lab results, clear user guidance, and published safety certifications.
For example, at Radiant Health, we build our therapy systems using this exact framework: grounded in clinical research, independently tested, and designed to elevate your experience with every use. We keep our safety reports readily available on our webiste.
Best Practices for Using Red & NIR Light
To make the most of red and near-infrared light therapy, follow these simple principles: Use regularly:
- 3–5x per week is ideal for skin and recovery benefits.
- Session length: 10–20 minutes per treatment area.
- Distance matters: Stay 6–12 inches from the light source for optimal penetration.
- Choose quality: Look for devices with accurate, consistent wavelengths (typically 630–660 nm for red, 810–850+ nm for NIR).
In Summary
Red and near-infrared light therapy isn’t just another wellness tool. It’s a way to reconnect with your body’s natural ability to heal. Whether you’re supporting skin renewal, easing muscle soreness, or recovering after intense activity, this therapy works gently beneath the surface to help restore balance, energy, and well-being.
At Radiant Health, we believe healing doesn’t have to be harsh or complicated. When you choose light therapy, you’re choosing consistency, simplicity, and a deeper kind of care — one that supports your body where it needs it most.
This is health that builds over time. Not a quick fix, but a quiet transformation. One that starts within, and moves outward.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How Often Should I Use Red or Near-Infrared Light Therapy?
Most people benefit from 3–5 sessions per week, lasting 10–20 minutes. For acute issues, daily sessions are safe and often recommended. - Does It Work for Wrinkles and Fine Lines?
Yes. Clinical studies show that red light increases collagen production and reduces the appearance of fine lines over consistent use. - Is Light Therapy Safe?
When used as directed, yes. It’s non-invasive, non-ionizing, and free of harmful UV. Radiant Health saunas use wavelengths that are clinically validated and safe for repeated use. - Can I Combine Light Therapy with Sauna Sessions?
Absolutely. In fact, many of our customers do. Combining the detoxifying heat of infrared sauna with the cellular stimulation of light therapy enhances recovery, mood, and skin vitality.
References
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5523874/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9808891/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11991943/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17566756/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21814736/

